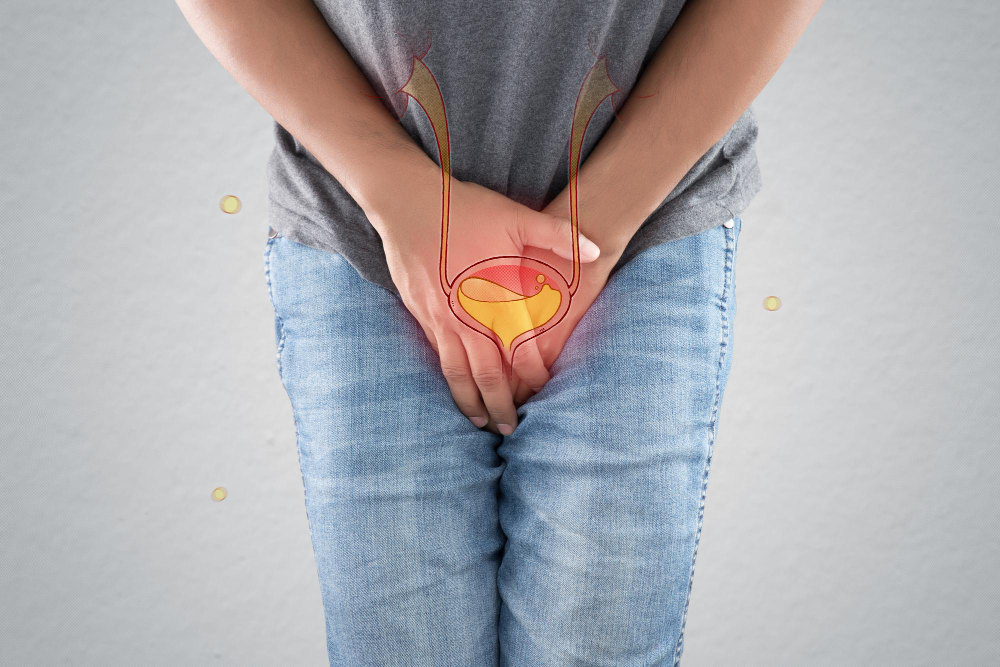
Overactive bladder is a common health issue that affects many people. It can cause sudden urges to urinate and may lead to frequent trips to the bathroom. Although it is not life-threatening, overactive bladder can disrupt daily life. In this blog, you will learn about the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for overactive bladder. We will also share tips to help you manage your bladder health.
What is Overactive Bladder?
Overactive bladder, often called OAB, is a condition where you feel a sudden and strong need to urinate. Sometimes, this urge is hard to control. As a result, you may need to use the bathroom more often than usual. In some cases, people may leak urine before they reach the toilet. Overactive bladder is not a disease, but it is a group of symptoms that affect bladder control.
Common Symptoms
Many people with overactive bladder notice changes in their bathroom habits. For example, you might:
However, not everyone will have all these symptoms. Some people may only notice one or two.
Causes and Risk Factors
There are several reasons why someone might develop overactive bladder. Sometimes, the cause is not clear. However, some common causes and risk factors include:
In addition, some medicines can make symptoms worse. For example, water pills may increase urine production.
How Overactive Bladder is Diagnosed
If you think you have overactive bladder, it is important to see a doctor. First, your doctor will ask about your symptoms and health history. Next, you may be asked to keep a bladder diary. This means you write down when and how often you urinate. Your doctor may also do a physical exam. In some cases, tests such as urine analysis or bladder scans are needed. These tests help rule out other problems, like infections or stones.
Treatment Options
There are many ways to treat overactive bladder. Your doctor will help you choose the best option. Common treatments include:
Sometimes, a mix of treatments works best. However, surgery is rarely needed and is only for severe cases.
Lifestyle Tips and Prevention
Simple changes can help manage overactive bladder. For instance, you can:
With these tips, many people find their symptoms improve. But, if symptoms continue, talk to your doctor.
When to See a Doctor
It is important to seek medical advice if you:
Early treatment can help prevent problems and improve your quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Conclusion
Overactive bladder can be bothersome, but help is available. With the right treatment and lifestyle changes, you can manage your symptoms. If you notice signs of overactive bladder, consult a urologist for personalized advice. Early care can make a big difference in your daily life.