Surgery
Surgery is a medical specialty that involves operative procedures to treat injuries, diseases, and deformities through manual or instrumental techniques. Surgical treatment encompasses a wide range of interventions, from minor outpatient procedures to complex operations requiring advanced technology and specialized training. Surgeons are trained to perform surgeries across various medical specialties, including general surgery, orthopedic surgery, neurosurgery, cardiovascular surgery, and more.
One of the primary goals of surgical treatment is to alleviate pain, restore function, and improve the quality of life for patients. Surgical interventions may be necessary to address acute conditions such as traumatic injuries, appendicitis, or acute abdominal conditions, as well as chronic conditions such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, or degenerative joint disorders.
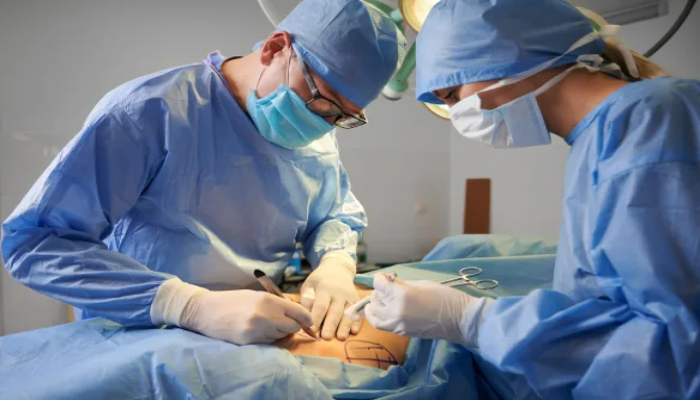
Surgical treatment typically begins with a thorough evaluation of the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as imaging studies or laboratory tests. Based on this assessment, the surgical team develops a personalized treatment plan tailored to the patient’s specific needs and circumstances.
Before surgery, patients may undergo preoperative preparation, which may include fasting, bowel preparation, medication adjustments, and other measures to optimize their health and reduce the risk of complications during and after surgery.
During the surgical procedure, the surgeon and operating room team work together to perform the necessary steps to address the patient’s condition. Surgical techniques can vary widely depending on the nature of the surgery and the specific anatomy involved. Surgeons may use traditional open surgical techniques or minimally invasive approaches such as laparoscopy or arthroscopy, which involve smaller incisions and specialized instruments.
surgery may be performed using advanced technology such as robotic-assisted surgery, which allows for greater precision and dexterity, particularly in complex procedures like prostatectomy or cardiac surgery.
Following surgery, patients are closely monitored in the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU) or intensive care unit (ICU) as needed. Pain management, wound care, and early mobilization are important aspects of postoperative care to promote healing and reduce the risk of complications such as infection or blood clots.
Recovery from surgery can vary depending on the type and complexity of the procedure, as well as individual factors such as age, overall health, and the presence of underlying medical conditions. Patients may require ongoing rehabilitation, physical therapy, or other supportive care to regain function and optimize their recovery.
treating specific conditions, surgical treatment may also play a preventive role in certain cases. For example, prophylactic surgeries such as mastectomy for high-risk breast cancer patients or appendectomy for patients with a history of recurrent appendicitis may be recommended to reduce the risk of future complications or disease progression.
surgical treatment is a vital component of modern medicine, offering patients the opportunity to overcome health challenges, restore function, and improve their overall well-being. It requires a collaborative effort among surgeons, anesthesiologists, nurses, and other healthcare professionals to ensure safe, effective, and compassionate care for patients undergoing surgical procedures.

